本篇目標:
- ReplicaSet - rs (副本集)
- Deployment - deploy (部署)
- StatefulSet - sts (有狀態集合)
- StorageClass - sc (儲存類別)
- PersistentVolumeClaim - pvc (持久化儲存:聲明 - 存儲規格)
- PersistentVolume - pv (持久化儲存:實際存儲)
- DaemonSet - ds (守護集合)
ReplicaSet - rs (副本集)
ReplicaSet 是一個管理 pod 副本數量的控制器,他確保指定數量的 pod 執行中,並且在 pod 異常時,會自動重啟 pod。
目前好像沒有說法是對於該工具使用場景,
因為 Deployment 涵蓋到他的範疇,
此外自動擴展是 k8s 的目的之一,
而這會 固定 開幾個 pod… 需著想應用場景可以透過
kubectl get rs來取得ReplicaSet的資訊。
可以執行kubectl get pods來確認 pod 是否有如預期,開出對應的replicas數量。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: re-deploy
spec:
replicas: 3 # 開啟副本的數量
selector:
matchLabels:
app: replica-app # <- (1) 這邊要對應到 pod 的 label
template: # <- 根據 template 去產生 pod
metadata:
labels:
app: replica-app # <- (2) 這邊要對應到 pod 的 label
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-re
image: nginx
(1)跟(2)必須相同;不同會無法啟動。
> 在 production 環境中,不建議使用ReplicaSet,建議使用Deployment。
>Deployment提供了滾動更新(rolling update)、回滾(rollback)、擴展(scale)等功能。
使得我們可以更彈性的去部署應用,並且平穩且有效的運作。
Deployment - deploy (部署)
介紹完
ReplicaSet,接著來看Deployment。
他建構在ReplicaSet之上,提供了更多的功能,如:滾動更新、回滾、擴展等功能。
在內部使用ReplicaSet管理其應用程式的 pod。
主要功能:
- 滾動更新(
rolling update): 透過Deployment可以進行滾動更新,這樣可以確保應用程式的可用性。- 回滾(
rollback): 透過Deployment可以進行回滾,這樣可以確保應用程式的可用性。- 擴展(
scale): 透過Deployment可以進行擴展,這樣可以確保應用程式的可用性。- 版本控制(
version control): 部署實作版本控制,因此允許回到先前的特定版本。
這邊僅僅是建立一個
Deployment,並且指定replicas的數量。
透過kubectl get deploy可以取得Deployment的資訊。
透過kubectl get pods可以取得pod的資訊。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hello-deploy
labels:
learn: deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
hello: world
template:
metadata:
labels:
hello: world
spec:
containers:
- name: hello-nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources: # 這邊可以約束 pod 的資源使用 (optional)
limits: # 該資源最多能用到多少的資源。
memory: 512Mi
cpu: "1"
requests: # 建立這個資源最小需求。
memory: 256Mi
cpu: "0.2"
StatefulSet - sts (有狀態集)
- 或許在某些情況下,我們需要一個有狀態的應用程式,這時候就需要
StatefulSet來管理這些有狀態的應用程式。
來持久化的資料,確保資料的一致性。
像是:MySQL、PostgreSQL、MongoDB等等。- 提供有序的部署和維護應用程式,並且確保每個 pod 有唯一的識別名稱。
例如: 當建立資源時先建立後端資源隨後再建立前端資源… 當銷毀時,則是先銷毀前端資源,再銷毀後端資源。
StatefulSet(sts)->PersistentVolumeClaim(pvc)->PersistentVolume(pv)
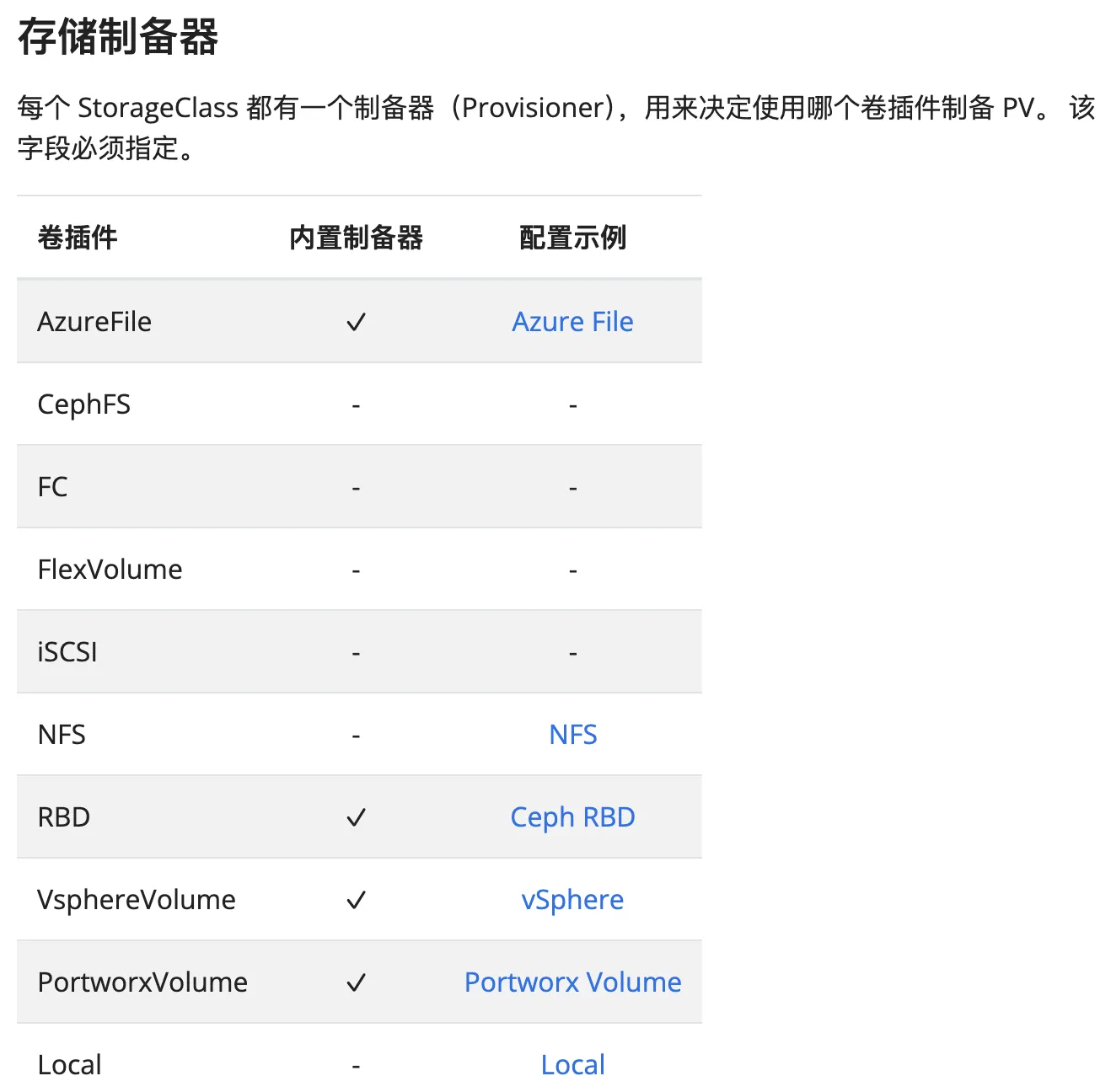
StorageClass - sc (儲存類別)
StorageClass是一個用來定義儲存類別的資源,他是一個對PersistentVolume的動態配置。
提供了一種描述存儲 類別 的對象,包括存儲可供部建的類型。
具體說,會有以下關鍵字段:
provisioner: 用來創建存儲的提供者parameters: 用來設定存儲的參數reclaimPolicy: 用來設定當 pv 釋放時,如何處理 pv 的內容volumeBindingMode: 用來設定 pv 的綁定模式allowVolumeExpansion: 用來設定是否允許擴展 pv 的大小
PersistentVolumeClaim - pvc (持久化儲存:聲明 - 存儲規格)
PersistentVolumeClaim是一個存儲資源的聲明,他是一個對PersistentVolume的請求。
PersistentVolumeClaim會對PersistentVolume進行請求,並且將PersistentVolume掛載到pod中。- accessModes: 有幾種模式
ReadWriteOnce-RWO: 只能被一個 pod 讀寫(個別獨立)ReadOnlyMany-ROX: 可以被多個 pod 同時讀取(唯讀)ReadWriteMany-RWX: 可以被多個 pod 同時讀寫(讀寫)ReadWriteOncePod-RWOP: 只能被一個 pod 讀寫(個別獨立),但是可以被多個 pod 同時讀取(唯讀)
持久卷: 裡面有相關資訊查詢,一方面是因為可以查看到
StorageClass的相關資訊,另一方面是可以查看到PersistentVolume的相關資訊。
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: simple-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: myapp
labels:
name: myapp
spec:
volumes:
- name: myapp-pvc
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: simple-pvc
containers:
- name: myapp
image: nginx:1.14
resources:
limits:
memory: "128Mi"
cpu: "500m"
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: "http-server"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/usr/share/nginx/html"
name: myapp-pvc
kubectl get pvc -A
PersistentVolume - pv (持久化儲存:實際存儲)
PersistentVolume是一個集群中的一個資源,他是一個實際的存儲資源。
可以先行建立PersistentVolume,並且在PersistentVolumeClaim中進行請求。
這樣可以達到對PersistentVolume的管理。
kubectl get pv -A
可以根據
PersistentVolumeClaim的例子中,看到pvc與pod的使用,
並且建立時pvc會產生pv,並且將pv掛載到pod中。
pvc 與 pv 的關聯
根據我的了解,有
pvc與pv,感覺是pvc是對外暴露的 volume 約束,pv是一個真正存儲的地方。
且 pv 是可以被建立,當資源去請求pvc時,他會先去找可用的pv;如果滿足就會使用它。
但是如果沒有滿足,他會去建立一個新的pv來滿足pvc的需求。
DaemonSet - ds (守護集合)
針對節點,沒有 namespace
不管開了多少個 pod 也只會在每個節點開一個對應的 pod。
Log Shippers:Logstash,Vector,FluentD,Filebeat,Promtail
參考資料
- 了解 (ReplicaSet)rs & (StatefulSet)sts & (DaemonSet)ds
- kubernetes-example
- 配置 Pod 以使用 PersistentVolume 作为存储
結論
在學習的過程中,本想說一些觀念,但是發現自己理解的無法清楚的表達,
並且也有部份是緊密連結。導致Service Account又拖延至下篇,
並且本篇還有很多不足夠,包括了清晰理解、實作等等…
本篇有點差強人意,希望下篇可以講到Service Account並且清晰的表達目前所學。
下篇可能討論
本篇還是沒有談到 Service Account
- Service Account
- 以目前知識探討、嘗試實際自己寫出一個部署應用